In the dynamic world of electronics, Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of nearly every device. Among the various types of PCBs, rigid-flex and flex PCBs have emerged as revolutionary technologies. These innovations address the need for lightweight, compact, and durable designs in an array of industries, including automotive, medical, aerospace, and consumer electronics.
This guide delves into the latest advancements, applications, and benefits of rigid-flex and flex PCBs, shedding light on why they are indispensable to modern electronics.
Understanding Rigid-Flex and Flex PCBs
Flex PCBs are constructed using flexible substrates, such as polyimide, which allows them to bend and twist without compromising electrical performance. They are typically single-sided, double-sided, or multi-layered, depending on the complexity of the application.
Rigid-Flex PCBs, on the other hand, combine rigid and flexible substrates into a single design. This hybrid approach leverages the strengths of both rigid boards and flex circuits, offering enhanced reliability and compactness.
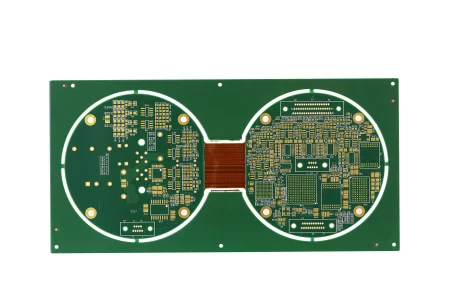
Key Innovations in Rigid-Flex and Flex PCBs
- High-Density Interconnect (HDI) Integration: HDI technology allows for higher circuit density, enabling more connections and components within a smaller footprint. This is particularly beneficial for compact devices like wearables and smartphones.
- Advanced Material Science: New materials, such as ultra-thin polyimide and liquid crystal polymers, enhance flexibility, thermal stability, and chemical resistance. These advancements ensure reliability in demanding environments, such as aerospace and automotive sectors.
- Enhanced Manufacturing Techniques: Techniques like laser drilling, roll-to-roll manufacturing, and additive processes have streamlined production, enabling precise and cost-effective designs for complex circuits.
- Integration of Embedded Components: Embedding passive and active components within the PCB layers reduces the need for external parts, resulting in smaller, lighter, and more efficient systems.
Applications of Rigid-Flex and Flex PCBs
Rigid-flex and flex PCBs are versatile solutions suitable for a range of applications:
- Consumer Electronics:
- Smartphones and tablets rely on flex PCBs for touch screens, cameras, and batteries.
- Wearables like fitness trackers benefit from the lightweight and flexible nature of flex circuits.
- Automotive Systems:
- Rigid-flex PCBs are integral to advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), infotainment, and power management units.
- Flex PCBs are used in LED lighting and sensors to accommodate unconventional shapes and space constraints.
- Medical Devices:
- Compact medical devices, such as pacemakers and hearing aids, utilize flex PCBs for their lightweight and biocompatible properties.
- Diagnostic tools and imaging equipment benefit from rigid-flex designs for high precision and durability.
- Aerospace and Defense:
- The high reliability and resistance to extreme conditions make rigid-flex PCBs ideal for avionics and satellite systems.
- Flex PCBs are used in lightweight communication devices and sensors.
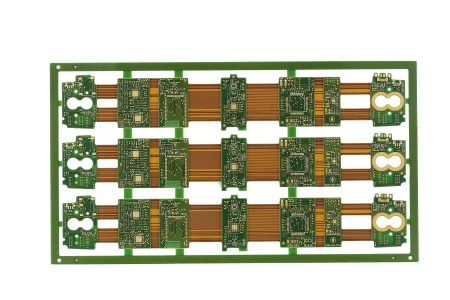
Benefits of Rigid-Flex and Flex PCBs
- Space and Weight Efficiency: Flex PCBs eliminate the need for connectors and cables, reducing the overall weight and volume of electronic systems.
- Design Flexibility: Engineers can create intricate three-dimensional designs, allowing circuits to fit into unconventional shapes and compact spaces.
- Durability and Reliability: These PCBs can withstand vibrations, bending, and extreme temperatures, ensuring long-term performance in harsh environments.
- Cost Savings: While initial manufacturing costs may be higher, the reduction in maintenance, assembly time, and component failures leads to significant cost savings over the product’s lifecycle.
Challenges and Solutions
Despite their advantages, rigid-flex and flex PCBs come with challenges:
- Complex Design Requirements: Designing these PCBs requires expertise and advanced software tools. Collaborative efforts between designers and manufacturers can mitigate this challenge.
- Higher Manufacturing Costs: The intricate processes involved in making rigid-flex and flex PCBs can be expensive. However, as manufacturing techniques evolve, costs are steadily decreasing.
- Material Selection: Choosing the right materials for flexibility and durability is critical. Consulting with material experts can ensure optimal performance.
Future Trends
The evolution of rigid-flex and flex PCBs continues to drive innovation:
- IoT Integration: With the proliferation of IoT devices, the demand for miniaturized, flexible, and reliable PCBs is skyrocketing.
- Wearable Technology: As wearable devices become more sophisticated, the need for ultra-thin and flexible PCBs will grow.
- Sustainability: Eco-friendly materials and manufacturing practices are gaining traction, aligning with global sustainability goals.
- Hybrid Electronics: Combining rigid-flex PCBs with advanced packaging techniques will enable higher functionality in smaller devices.
Conclusion
Rigid-flex and flex PCBs are at the forefront of electronic innovation, providing unmatched versatility, reliability, and performance. As industries push the boundaries of technology, these advanced PCBs will remain critical enablers of progress. By embracing the latest advancements and overcoming challenges, engineers and manufacturers can unlock the full potential of rigid-flex and flex PCBs, paving the way for a smarter and more connected future.
XPCB Limited is your go-to partner for turning your PCB dreams into reality. Our streamlined PCB manufacturing process, combined with quick-turnaround prototyping and turnkey PCBA services, ensures that your projects come to life with ease. Trust in our expertise and dedication to quality as we help you achieve your PCB goals. Join us and experience the difference with XPCB Limited.









