- +86-755-23012705
- Building 3, Jinfeng Industrial Park, Fuyong Street, Baoan District, Shenzhen ,China
- [email protected]
Printed circuit board, abbreviated PCB, also known as PWB, printed wire board. It is based on insulation board, cut into a certain size, attached to at least one conductive pattern, and arranged with holes (such as element holes, fastening holes, metallized holes, etc.) Circuit Board is an important parts of electronics, is the support body of electronic components, is the carrier of electrical connection of electronic components. It is called “printed” circuit board because it is made using electronic printing technology.
Almost every electronic device, such as electronic watches, calculators, computers, communication electronic devices, military weapon systems, etc., as long as there are integrated circuit electronic components, for their electrical interconnection, they use printed circuit boards.
The inventor of the printed circuit board was An Austrian named Paul Eisler, who used it in a radio device in 1936. In 1943, the Americans popularized the technology in military radios. In 1948, the Invention was officially approved for commercial use in the United States. It was only in the Mid-1950s that the printed circuit board technology was widely adopted.
Before the appearance of printed circuit boards, the interconnection between electronic components was realized by direct connection of wires. Now, the circuit board exists only as an effective experimental tool; The printed circuit board has occupied the absolute dominant position in the electronic industry.
According to the number of circuit board layers, printed circuit board can be divided into single sided, two-layer, 4-layer board, 6-layer board and other multi-layer circuit board.
As printed circuit board is not a general-end/terminal product, so the definition of the name is somewhat confusing. For example, the motherboard used in personal computers, called the motherboard, but cannot be directly called the circuit board, although there is a circuit board in the motherboard, but not the same, so the two related to the evaluation of the industry cannot be said the same.
Another example, the news media calls it an IC board because an integrated circuit component is mounted on a circuit board, but it is not essentially the same as a printed circuit board.
Single sided PCB:
A single-sided PCB assembly is mounted on one side only, and the other side is used for copper wiring. A thin copper foil layer is applied to one side of the substrate and a welding mask is applied to provide insulation. Finally, screen printing is used to provide component marking information on the PCB.
These single-layer PCBS are easy to design and manufacture on a large scale, are in high demand and are cheap to buy. Very commonly used in household products such as juicers/mixers, charging fans, calculators, small battery chargers, toys, TV remote controls, etc.
Double side PCB:
Double-sided PCB is a PCB with copper layer on both sides of the substrate. The lead THT components are installed in these through holes. These holes connect one side of the assembly to the other through a copper track. Component leads pass through the holes, excess leads are cut by a cutter, and leads are welded to the holes. This is all done manually.
SMT components can also be included. SMT components do not need holes, solder pads are made on the PCB, and SMT components are fixed on the PCB by reflow welding. SMT components take up very little space on the PCB, so more free space can be used on the board to achieve more functions.
Double-sided PCB for power supply, amplifier, DC motor driver, instrument circuit, etc.
Multi-layer PCB:
Multilayer PCBS are made of two layers of PCBS sandwiched between dielectric insulation layers to ensure that the boards and components are not damaged by overheating. Multilayer PCBS come in a variety of dimensions and layers, from 4 to 36layer.The more layers, the more complex the circuit, the more complex the PCB layout design. Multilayer PCBS usually have independent grounding, power layer, high speed signal layer, signal integrity consideration, thermal management.
Common applications are military requirements, aerospace and aerospace electronics, satellite communications, navigation electronics, GPS tracking, radar, digital signal processing and image processing.
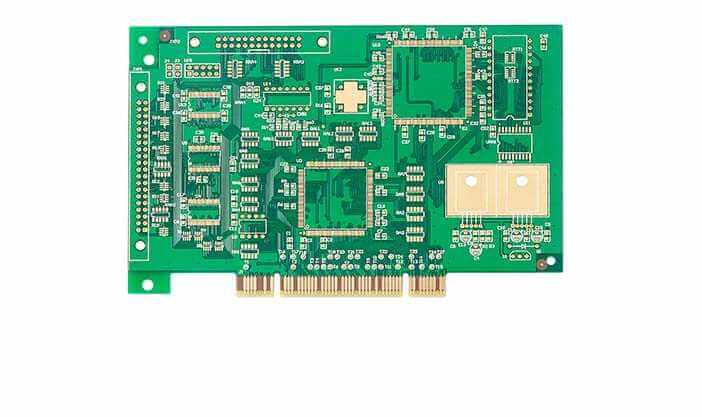
Rigid PCB:
Rigid PCBs have solid substrates such as FR-4, Rogers, phenolic and epoxy. These plates do not bend or twist, but can remain in shape for many years for 10 or 20 years. This is why many electronic devices have a long life because of the rigidity, solidity and rigidity of rigid PCBS.
PCBS are rigid pcb in computers and laptops, and many televisions, LCDS and LED TVS are made of rigid PCBS. All of the above single-sided, double-sided and multi-layer PCB applications are also available for rigid PCB applications.
Flex PCB:
Flexible PCB is flexible and can be easily bent. They are elastic, have high heat resistance and excellent electrical properties. Flex PCB substrate materials depend on performance and cost. Common substrate materials for Flex PCB are polyamide (PI) film, PET (PET) film, PEN and PTFE.
Flex PCBS differ from rigid PCBS in that they are light in weight but have very low tear strength. But they can be folded or wrapped around corners, taking up less space than their rigid counterparts.

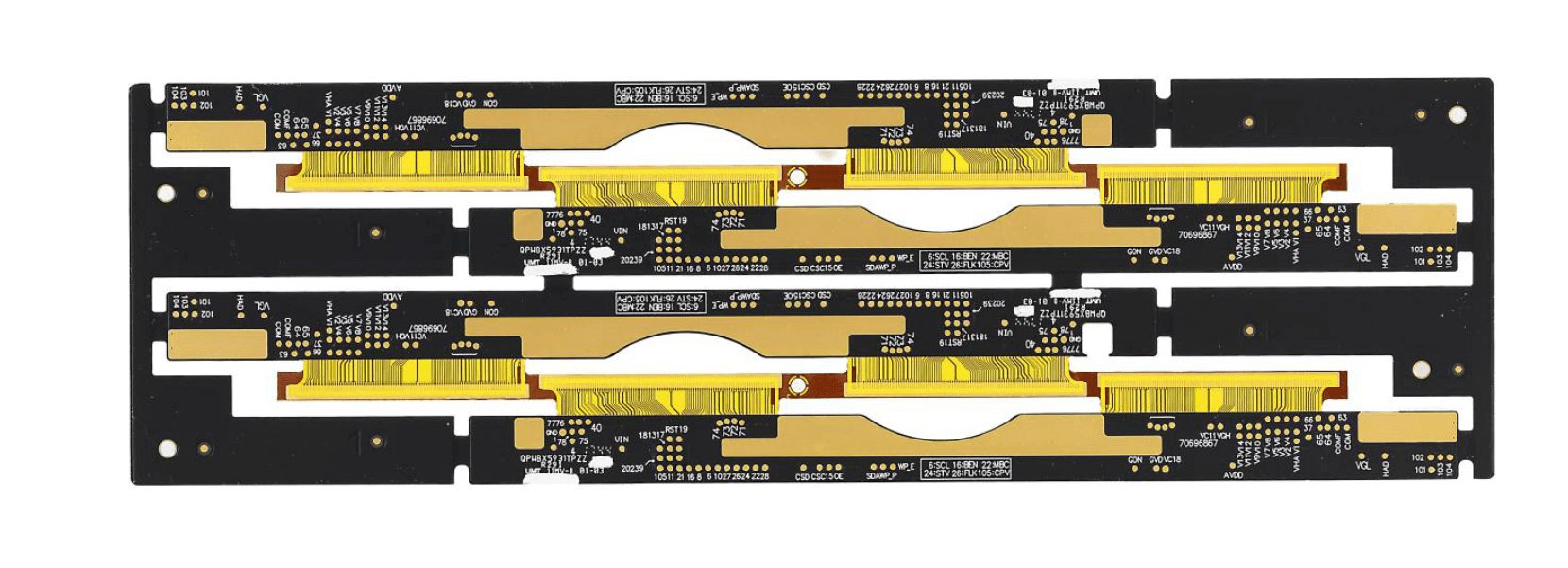
Rigid-Flex PCB:
The rigid-flex PCB is important in many space and weight constrained applications. For example, in a camera, the circuit is complex, but the combination of rigid and flexible PCB will reduce the number of components and the size of the PCB. The wiring of two PCBS can also be combined on a single PCB. Common applications are digital cameras, mobile phones, cars, laptops and devices with moving parts.
High speed PCB:
High speed or high frequency PCB is used for applications involving signal communications with frequencies higher than 1GHz. In this case, signal integrity issues come into play. Materials for hf PCB substrates should be carefully selected to meet design requirements. Common materials are polyphony (PPO) and polytetrafluoroethylene. It has stable dielectric constant and small dielectric loss. They are low in water absorption but high in cost. Many other dielectric materials have variable dielectric constants, resulting in impedance changes that distort harmonic and digital signal loss and signal integrity loss.
Aluminum PCB:
Alu PCBs substrate material has the property of effective heat dissipation energy. Due to low thermal resistance, aluminum – based PCBS are more effective than their copper – based counterparts in cooling. It gives off heat in the air and in the hot junction area of the PCB. Many LED lamp circuits, high brightness LEDS are made of aluminum backed PCB.
Aluminum is a rich metal and is cheap to extract, so PCB costs are low. Aluminum is recyclable and non-toxic, making it environmentally friendly. Aluminum is rugged and thus reduces damage during manufacturing, transportation and assembly.
All of these features make aluminum based PCBS beneficial for high current applications such as motor controllers, heavy duty battery chargers and high brightness LED lights.






XPCB Limited is a premium PCB & PCBA manufacturer based in China.
We specialize in multilayer flexible circuits, rigid-flex PCB, HDI PCB, and Rogers PCB.
Quick-turn PCB prototyping is our specialty. Demanding project is our advantage.
Tel : +86-136-3163-3671
Fax : +86-755-2301 2705
Email : [email protected]
© 2024 - XPCB Limited All Right Reserve
